3260. How many?
Preparing for the
calculus exam, Petya spread out n different cheat sheets in front of
himself. They were his salvation, as throughout the entire semester Petya had
never bothered to properly study the material. There were so many cheat sheets
that they didn’t fit into any pocket. Therefore, Petya decided to calculate the
maximum number of cheat sheets he could take with him to the exam. And then the
question arose: how many ways are there in total to choose the required number
of cheat sheets?
Input. Contains the total number of cheat sheets n (1 ≤ n ≤ 12) and
the number of cheat sheets k (0 ≤ k
≤ n) that Peter can take with
him.
Output. Print the number of ways to choose k cheat sheets from n.
|
Sample input 1 |
Sample output 1 |
|
3 2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
Sample input 2 |
Sample output 2 |
|
4 1 |
4 |
SOLUTION
combinatorics
Algorithm analysis
To compute the binomial coefficient, you can use the following
formula:
![]() =
= =
= ![]()
Declare a variable res and initialize it with a value of 1.
Then multiply res by n and divide the result by 1. After that
multiply res by n – 1 and divide by 2. Continue this process of multiplication and
division k times (the numerator and
denominator of ![]() after simplification
by (n – k)! contain k
factors).
after simplification
by (n – k)! contain k
factors).
For the recursive implementation of the binomial coefficient,
use the following formula:
![]() =
= 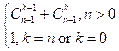
Algorithm implementation
The Cnk function returns the
binomial coefficient using an
iterative method.
int Cnk(int
n, int k)
{
int res = 1;
for(int i = 1; i
<= k; i++)
res = res * (n - i
+ 1) / i;
return res;
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);
Compute and print the answer.
res = Cnk(n,k);
printf("%d\n",res);
Algorithm implementation – recursion
The Cnk function returns the
binomial coefficient using a recursive method.
int Cnk(int
n, int k)
{
if (n == k) return 1;
if (k == 0) return 1;
return Cnk(n - 1, k - 1) + Cnk(n - 1, k);
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);
Compute and print the answer.
res = Cnk(n,k);
printf("%d\n",res);
Algorithm implementation – recursion with
memorization
Declare a dp array
to store the values of the binomial coefficient: dp[n][k] = ![]() .
.
int dp[35][35];
The Cnk function returns the
binomial coefficient using a recursive method. Memoization technique is used.
int Cnk(int
n, int k)
{
if (n == k) return 1;
if (k == 0) return 1;
if (dp[n][k] != -1) return
dp[n][k];
return dp[n][k] = Cnk(n - 1, k - 1) + Cnk(n - 1, k);
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);
Initialize the dp array.
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
Compute and print the answer.
res = Cnk(n,k);
printf("%d\n",res);
Java implementation – recursion
import
java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int Cnk(int n, int k)
{
if (n == k) return 1;
if (k == 0) return 1;
return Cnk(n - 1, k - 1) + Cnk(n - 1, k);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int k = con.nextInt();
int res = Cnk(n,k);
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Java implementation – recursion with memorization
import
java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int dp[][];
static int Cnk(int n, int k)
{
if (n == k) return 1;
if (k == 0) return 1;
if (dp[n][k] != -1) return dp[n][k];
return dp[n][k] = Cnk(n - 1, k - 1) + Cnk(n - 1, k);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int k = con.nextInt();
dp = new int[n+1][k+1];
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
Arrays.fill(dp[i],-1);
int res = Cnk(n,k);
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation – comb
To compute the binomial coefficient, we shall use the built-in function
comb(n, k) = ![]()
import math;
Read the input data.
n, k = map(int, input().split())
Compute and print the answer.
res = math.comb(n, k)
print(res)
Python implementation – factorial
The fact(x) function computes the factorial of the number x.
def fact(x):
if x:
return fact(x - 1) * x
else:
return 1
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
n, k = map(int, input().split())
Compute and print the answer.
res = fact(n) // (fact(k)
* fact(n - k))
print(res)
Python implementation – recursion
with memorization
The Cnk function returns the
binomial coefficient using a recursive method. Memoization technique is used.
def Cnk(n, k, dp):
if n == k: return 1
if k == 0: return 1
if dp[n][k] != -1: return dp[n][k]
dp[n][k] = Cnk(n - 1, k - 1, dp) + Cnk(n - 1, k, dp)
return dp[n][k]
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
n, k = map(int, input().split())
Declare a dp list
to store the values of the binomial coefficient: dp[n][k] = ![]() .
.
dp = [[-1] * 35 for _ in range(35)]
Compute and print the answer.
res = Cnk(n, k, dp)
print(res)